Maxim’s digital IO IC helps SICK AG’s safety scanner reduce LiDAR size
“However, in the past ten years, due to the development of machine learning, self-driving cars and robotics, the penetration rate of LiDAR has increased substantially. These fields have helped promote the development of LiDAR technology, which has greatly reduced the cost and size, and even the iPhone can be equipped with this technology.
“
Maxim Integrated and SICK AG have jointly launched the industry’s smallest LiDAR security scanner.
For many designers, the biggest disadvantage of using LiDAR technology in applications is the size and cost of the system.
However, in the past ten years, due to the development of machine learning, self-driving cars and robotics, the penetration rate of LiDAR has increased substantially. These fields have helped promote the development of LiDAR technology, which has greatly reduced the cost and size, and even the iPhone can be equipped with this technology.

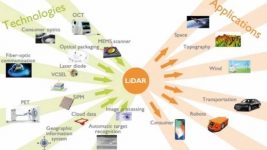
LiDAR technology types and applications. Image courtesy of Yole Développement.
Even with recent improvements, the technology still has room for further maturity, and the industry continues to promote this work. A key example comes from the collaboration between SICK AG and Maxim Integrated last week. This cooperation has further promoted the development of the LiDAR field, forming what the two companies call the smallest LiDAR security scanner in the industry.
SICK AG’s nanoScan3
SICK AG’s latest product nanoScan3 is an industrial security scanner based on LiDAR system.

nanoScan3 is the latest LiDAR scanner from SICK AG. Image courtesy of Maxim Integrated.
The size of nanoScan3 is 106.6 mm x 80 mm x 117.5 mm, which is 50% less than previous generations. It is specially developed for compact mobile platforms that work in harsh industrial environments.
For this reason, the scanner is built into a compact and durable metal housing, making it highly resistant to interference, including dust, pollution and ambient light. nanoScan3 uses rotating LiDAR technology and runs at a speed of 80,000 pulses per revolution, which can achieve a scanning angle of 275 degrees and a protection area of 3 meters.
In addition, according to the data sheet, the system is powered by a 24 VDC rail with a power consumption of up to 3.9 W, which does not seem to be an IoT figure; however, in the industrial field, it is reasonable.
When reviewing this new innovation, the main focus is the miniaturization of LiDAR scanners, but how did Maxim and SICK AG achieve it?
Realize miniaturization
According to the two companies, the size of the module has been reduced by 50% compared to previous generations of products, which directly stems from Maxim’s configurable digital IO technology.
Specifically, nanoScan3 uses MAX14914 software configurable digital IO, this component allows designers to greatly reduce the number of components and peripherals. Specifically, MAX14914 enables designers of SICK AG to remove six external components and several peripherals and integrate them into one IC, thus saving space and power.
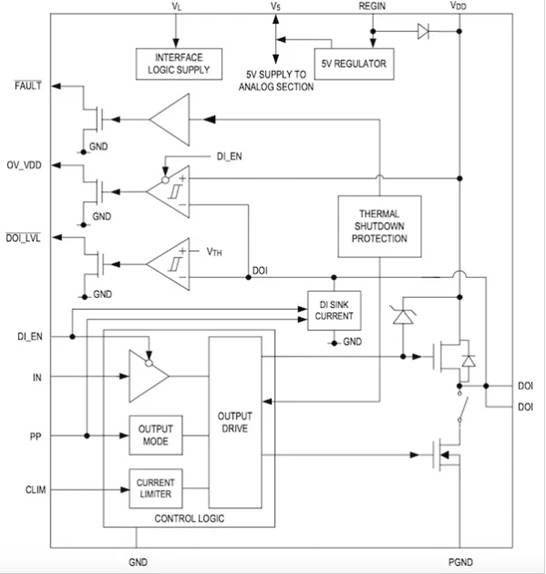
Block diagram of MAX14914.Image courtesy of Maxim Integrated
On this basis, Maxim also attributed the reduction in size to MAX22191, which was also used in nanoScan3. This IC is an industrial digital input device that can convert 24 V industrial switching signals into 3.3 V or 5 V CMOS-level output. The key to the MAX22191 is that it is used as a single-channel, parasitic-powered digital input. Maxim claims that this feature makes the nanoScan3 miniaturized.
A developing field
The field of LiDAR technology is accelerating. Cooperation such as Maxim and SICK AG shows that this growth will accelerate, especially as more LiDAR applications rise, and the demand for miniaturization further increases.
As applications such as self-driving cars, robotics, and computer vision continue to be integrated into our daily lives, it seems that LiDAR will do the same.
The Links: LM170E03-TLB2 https://www.slw-ele.com/ltm10c209h.html“> LTM10C209H



